

Dr. Shakti P Choudhury Is A Renowned And Highly Experienced Gastroenterologist In Odisha.
House Nos Mig 34, Near Fire Station Square, Baramunda, Bhubaneswar, 751003, In
+91-7835056101
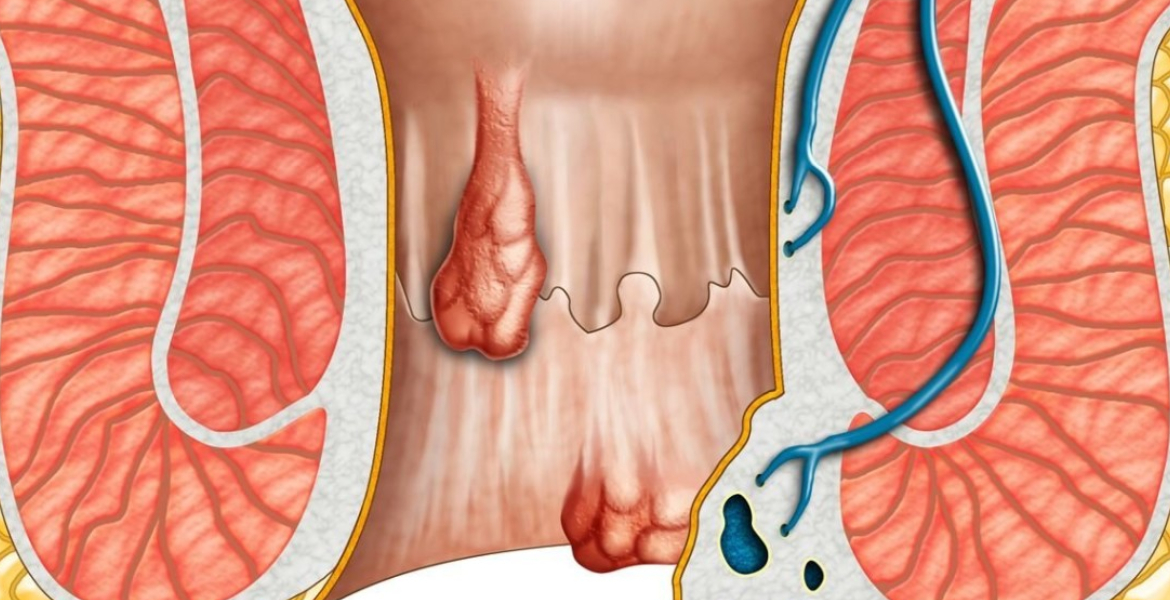

Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They can develop internally inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or externally under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids). Piles are a common condition and can occur due to various factors, including straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, pregnancy, and aging.
Rectal bleeding, typically during bowel movements, which may appear as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Itching or irritation in the anal area.
Pain or discomfort, especially during bowel movements.
Swelling or lumps around the anus.
Leakage of feces or mucus.
Internal Hemorrhoids: These occur inside the rectum and may not cause any noticeable symptoms unless they prolapse (protrude) outside the anus during bowel movements.
External Hemorrhoids: These form under the skin around the anus and can be painful, especially if they develop blood clots (thrombosed hemorrhoids).
Rectal bleeding, typically during bowel movements, which may appear as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Itching or irritation in the anal area.
Pain or discomfort, especially during bowel movements.
Swelling or lumps around the anus.
Leakage of feces or mucus.
Straining during bowel movements.
Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
Sitting or standing for prolonged periods.
Obesity or being overweight.
Pregnancy and childbirth.
Aging, as the tissues supporting the veins weaken over time.
Lifestyle modifications, such as increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, and avoiding straining during bowel movements.
Topical treatments, such as over-the-counter creams or suppositories to relieve itching, pain, and swelling.
Sitz baths, which involve soaking the anal area in warm water to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
Procedures to remove or shrink piles, such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, infrared coagulation, or surgical removal (hemorrhoidectomy) for severe cases.
Maintain a high-fiber diet to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
Avoid straining during bowel movements.
Practice good anal hygiene, such as gently cleaning the anal area with moist wipes or a bidet instead of harsh toilet paper.
Exercise regularly to improve circulation and bowel function.